Flu, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), and other respiratory viruses
Protect yourself and your family from viruses this season
Contrast Accessibility
Animation Control
Contact & Help
Contact UsJacksonville Center
Search
Quick Search

Protect yourself and your family from viruses this season
Respiratory viruses are germs that can cause infections in your lungs, airways, and other parts of your respiratory system. Common types of these include influenza (flu), COVID-19, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
These viruses can spread through the air when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. Close contact with someone who's infected can also transmit the virus, as well as touching surfaces that have the virus on them and then touching your face.
Respiratory viruses are more common in certain groups, including infants and young children, especially those in daycare or school; older adults with weakened immune systems; people with underlying health conditions, such as asthma, heart disease, or diabetes; people with compromised immune systems; and pregnant women.
Vaccines are widely recognized by health professionals as safe and effective for helping prevent the spread of respiratory viruses, reducing hospitalization, and protecting vulnerable individuals. Here are five tips to help avoid respiratory viruses:
The flu, also known as influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by a virus. It affects the nose, throat, and lungs, and can range from mild to severe.
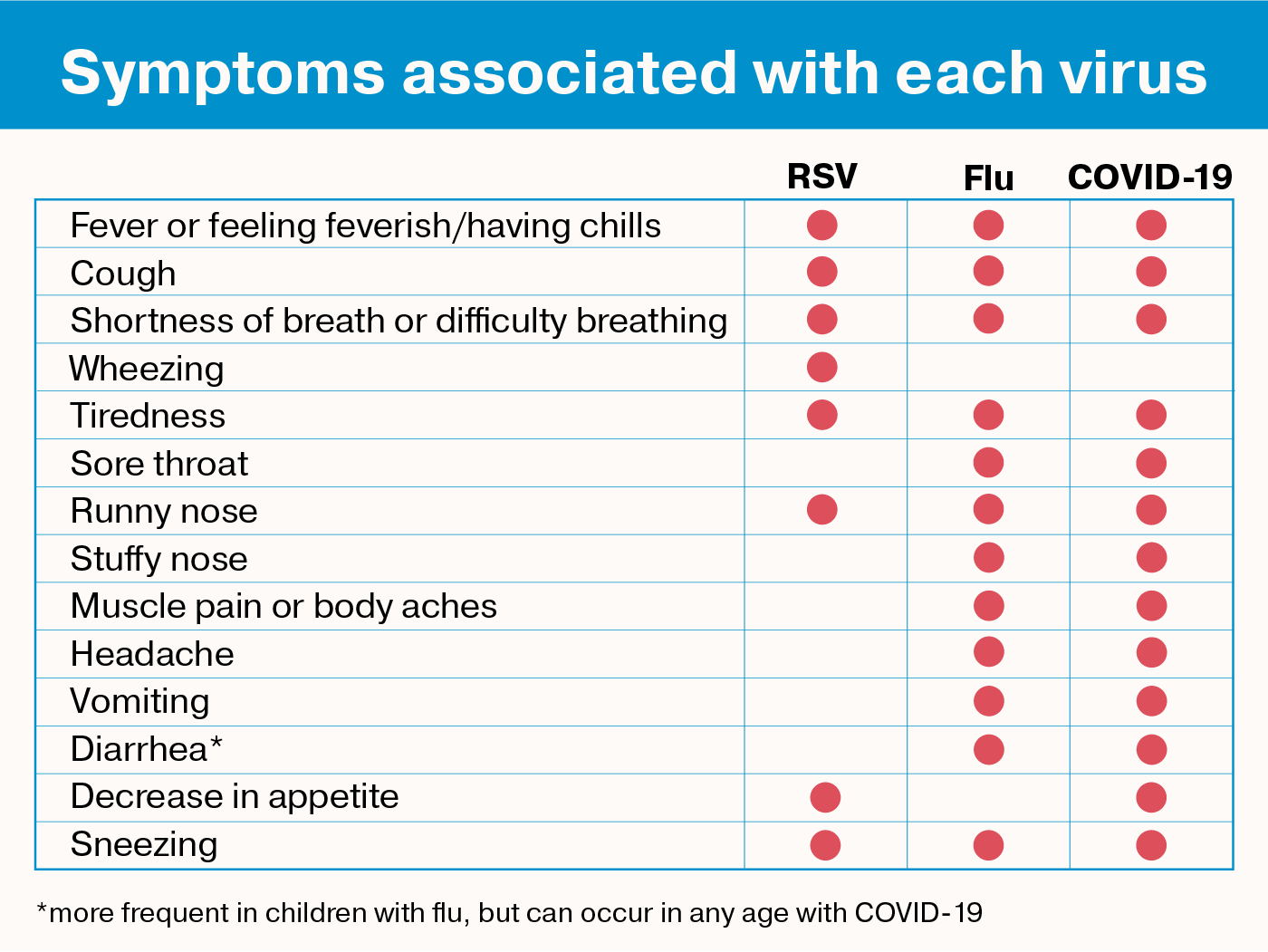
The symptoms can be similar, but there are key differences. The flu comes on abruptly and commonly includes a fever, body aches, fatigue, and headache. A cold is a more gradual onset, rarely causes a fever and commonly includes sneezing, a stuffy nose, and sore throat. For more information on the difference between different respiratory viruses, view the chart below.
While there's no way to completely prevent the flu, you can decrease your risk by following the five tips listed above. Health professionals consider the flu vaccine to be safe and effective for helping prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and even death from flu complications. Watch this video for more information on the flu shot.
You can’t get the flu from the flu shot. The injected flu vaccine doesn’t have any living virus and cannot cause the flu. Watch this video to learn more.
Most Florida Blue members can get a flu shot and other preventive vaccines at no extra cost when they go to an in-network doctor or pharmacy.
According to the CDC, a routine annual flu shot is recommended for everyone age 6 months and older. This also includes high-risk groups, like older adults, children, and pregnant women, and their caregivers. Watch this video to learn more. We encourage individuals and caregivers to speak with their doctor to discuss any question or concerns about the benefits of the flu vaccine.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common virus that has symptoms like the common cold and affects the lungs and breathing passages.
RSV is usually mild for most people. But some people get complications of RSV like bronchitis and pneumonia. Most RSV infections go away on their own in a week or two, but sometimes more serious symptoms can happen, which can cause shortness of breath and low oxygen levels. RSV can also lead to worsening of other medical conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or congestive heart failure.
While most people, including infants, usually develop only mild symptoms like a common cold, RSV can be severe and even life-threatening, especially for young infants and older adults.
RSV is the leading cause of hospitalizations for infants and older babies at higher risk, per this article in the National Institutes of Health.
You can decrease your risk of getting RSV by following the prevention tips above. There are also RSV vaccination options available for those who are at an increased risk of getting RSV. Speak with your primary care doctor to
to discuss any questions about the benefits of vaccination.
COVID-19 is a viral illness caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It is a type of upper respiratory infection (URI) that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can spread quickly.
Viruses are constantly changing, including the virus that causes COVID-19. These changes occur over time and can lead to the emergence of variants that may have new characteristics, including different ways of spreading. Slowing the spread of the virus, by protecting yourself and others, can help slow new variants from developing.
You can reduce your risk of getting COVID-19, by following the prevention tips above. There are also vaccines and boosters available for COVID-19. Speak with your primary care doctor to discuss any questions about the benefits of vaccination.
While all three respiratory viruses have similar symptoms, the only way to confirm a diagnosis is by medical testing. This helps identify the virus to determine the best way to treat it.